Written by - Monu Dalal
Introduction to Brick :-
Brick is defined as a material used for building construction to make walls, pavements and other masonry works. It is a type of block unit that is composed of clay. Bricks are commonly made from clay and shale.
- Clay is upper or smooth surface on earth and contains various quantities of chalk, iron, manganese etc. - Shale is soft sedimentary rock that formed from consolidated mud or clay and can be split easily into fragile plates.
Types of Bricks :- Bricks are categorised in different types. Let's discuss all in detail.
1. Sun dried/Unburnt bricks - These are simply clay formed bricks, passes through some common steps are preparation of clay, molding and drying. These bricks are less durable and used for temporary structure.2. Burnt Clay Bricks - These bricks are of good quality and burn in fire in chimneys to make strong/hard. These are classified in four categories(size - 230x115x75mm)
(a) First class bricks - these bricks are of good quality, table-moulded and of standard shape with smooth/Straight surface. (b) Second class bricks - these are ground moulded and burnt in kilns with rough/irregular shape. Used where coating of plaster is provided. (c) Third class bricks - These bricks are moulded in ground and burnt in clamps with no hardness and irregular shape. They are placed where rainfall is not heavy for temporary use.(d) Fourth class bricks - These bricks are used as aggregate for concrete in floors,roads and foundations etc with irregular shape,dark colour and are over burnt.
3. Fly Ash Bricks - These bricks contains calcium oxide used in cement production, and manufactured by using fly ash and water. They have better properties than clay bricks like resistant and lightweight etc.(size - 230x150x100mm)
4. Concrete Bricks - These bricks are manufactured by using concrete with ingredients as cement, sand, coarse aggregates and water. And these bricks are also manufactured in sizes as required.(size - 600x200x100mm)
5. Engineering Bricks - These bricks having high compressive strength and used in basement and damp proof course.
6. Sand Lime Bricks - These bricks are made up of sand and lime and for several purposes in construction.(size - 190x90x90mm)
Uses of Bricks :-
Bricks are uses for different purposes in construction.
(I) Wall Construction
(II) Construction of Floors
(III) Foundation Construction
(IV) Staircase
(V) Arches Construction
(VI) Surkhi Manufacture
Properties of Bricks -
As bricks are categorised in different types and uses for different purposes in construction, having some properties. These properties are from their use and formation. Properties are colour, Texture, Porosity, Absorption, Size Variation, Compressive strength, Fire resistance etc.
Advantages of Bricks :-
- Economical/Affordable
- Better thermal insulation
- Low maintenance cost
- Good sound absorption
- Size enables easy handling
- Masonry is easier/ stronger
Disadvantages of Bricks :-
-Can't used in high seismic zone
- Time consuming construction
- Less tensile strength
- Rough surface cause mould growth
- Absorbs water easily causes fluorescence
Characteristics of Bricks :-
- Brick should be of true size and shape with plain surface and edges.
- Should be free from cracks
- Good bricks and truely burnt for hardness and durability.
- Ringing sound emits when two bricks stuck together.
- Should not absorb water more than 22%.
- Brick should not break when dropped from about 1m height on hard surface.
- Bricks should have low thermal conductivity and be sound proof.
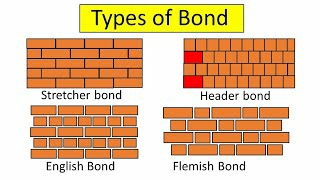
Brick Bonds :-
Brick Bonds are defined as the bonds use to form construction pattern and enhance its stability. Their are commonly four types of bonds are in trend.
1. Stretcher bond - used for single brick wall.
2. Header bond - bricks laid flat with short end of brick exposed.
3. English bond - this bond comprises of alternative courses of headers and stretcher.
4. Flemish bond - it can be formed by one brick header and other brick stretcher in a row.
Raw Materials of Brick :-
- mixture of loam, mud, sand, and water for clay bricks
- silica sand, quick lime, water for sand Lime bricks
- powdered portland cement, water, sand, and gravel for concrete bricks
- fly ash sand, stone dust, sludge lime, gypsum for fly ash bricks
- fly ash, sand, lime powder, cement, gypsum for aac bricks
Manufacturing Process :-
Manufacturing of bricks consists of various stages are -
- Unsoiling : 20cm to 30cm depth top layer removed as it contains impurities.
- Digging : clay dug out from ground is spread on levelled ground about 60cm to 150cm.
- Cleaning - stones and vegetable matter etc. of clay are converted into powder form.
- Weathering : it is process like seasoning to make clay soft.
- Blending : clay is made loose and any ingredient to be added to it is spread out at top .
- Tempering/Burning : clay is brought to a proper degree of hardness in heat.
Test on brick :-
To check the strength and usability in construction some test should be done, tests are Absorption, Hardness, Crushing strength, Presence of salts, Shape and size, Soundness, Structure must be done in testing.







Thank you
ReplyDelete